|
This is used for preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) of the
fertilized embryo. A micromanipulator is used to remove one or often two cells
from an embryo, usually when it is at the 10-12 cell stage.
|
|
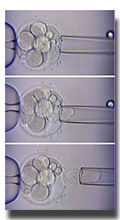 |
These cells are then examined for genetic or chromosomal errors.
This technology can be of profound importance
clinically. Hence, couples whose offspring have a high chance of inheriting a
genetic disorder may have their embryos screened. While embryos can have their
sex determined through this procedure, it is illegal in India, except in cases
of sex chromosome-linked disorders.
|
|

|
|
|
|
The assisted hatching procedure involves making a small hole in
the zona pellucida (a protective layer) that surrounds the embryo. Before an
embryo implants into the uterus it must hatch from the zona pellucida. There is
some evidence that in some women the zona becomes toughened, restricting the
embryo to hatch. It is thought that making a small hole in the zona may make it
easier for hatching to occur.
|
|
This is done just before the embryos are replaced, whether they
are fresh or frozen/thawed, using chemical, mechanical or laser methods and a
micromanipulation technique.The process will damage about 1% of embryos.
|
|
No benefit has been reported when assisted hatching was offered to all patients
undergoing ART procedures.
Assisted hatching may be beneficial to
-
Women over 39 years (elevated FSH levels) and using their own eggs.
-
Women who had recurrent failure of embryo implantation
-
Women whose embryos exhibit thick zona pellucida.
|

|